The evolution of the Toronto Power Generation Station and its significant role in the development of hydroelectric power in Canada.
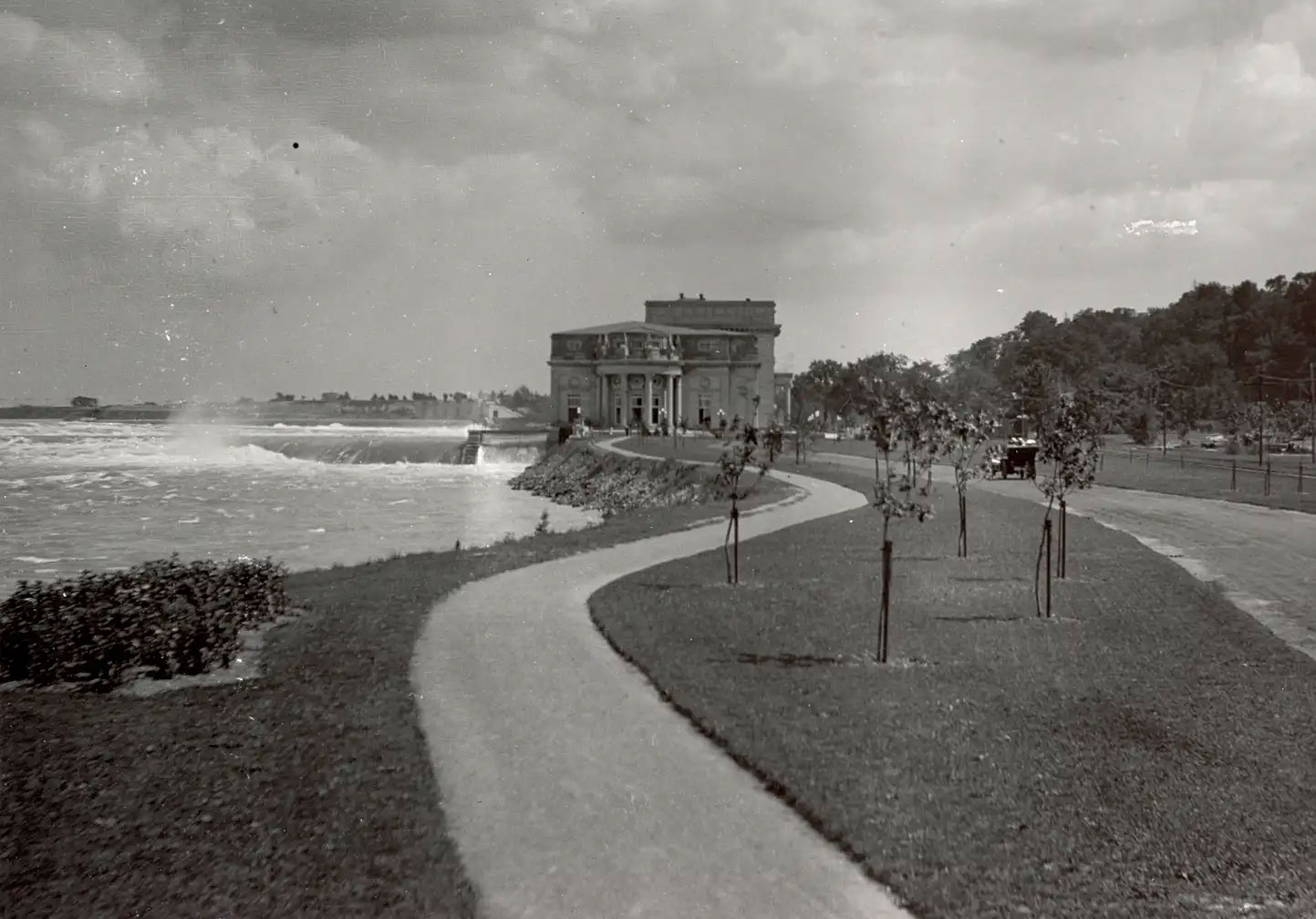
The Toronto Power Generation Station, located along the majestic Niagara River in Niagara Falls, Ontario, stands as a testament to Canada’s pioneering efforts in harnessing the power of water for electricity. As the first wholly Canadian-owned hydroelectric facility at Niagara Falls, it played a crucial role in shaping the development of business, industry, and technology in Ontario and Canada. This article delves into the history and significance of the Toronto Power Generation Station, highlighting its remarkable achievements and enduring legacy.
Construction and Design
Exploring the architectural marvels and engineering triumphs of the Toronto Power Generation Station.
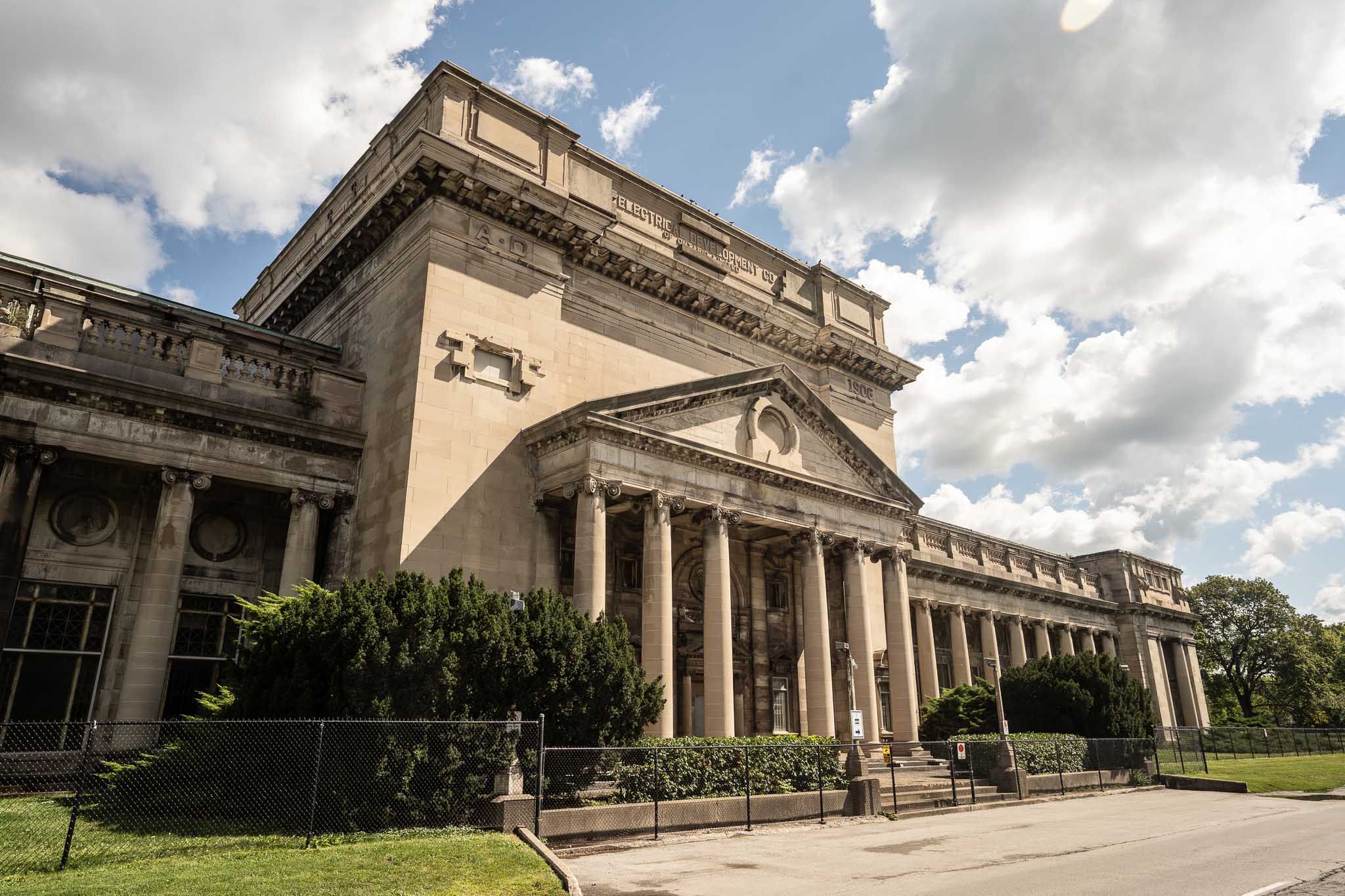
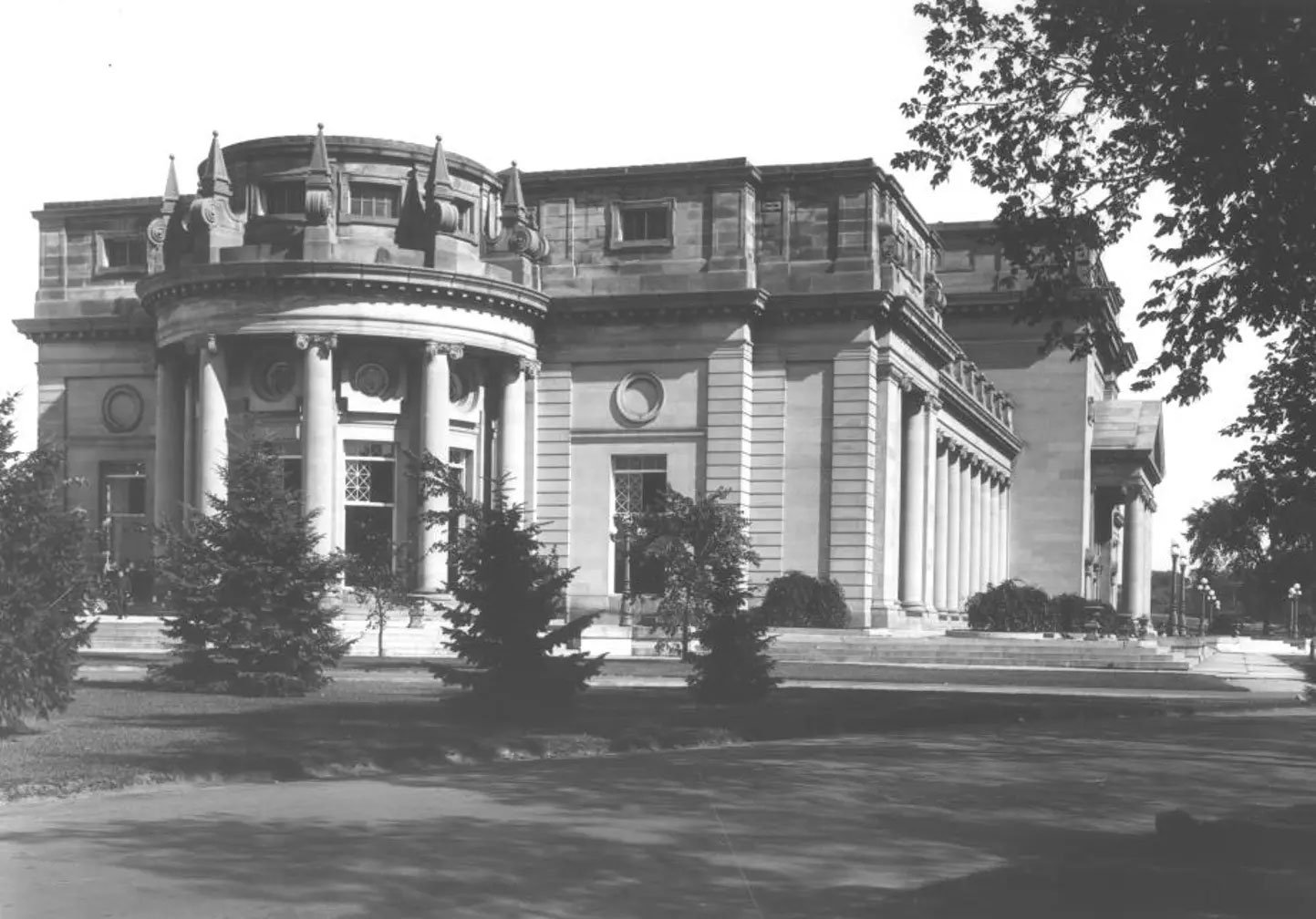
The construction of the Toronto Power Generation Station began in 1903 and lasted a decade, with the powerhouse serving as the centerpiece of this monumental project. Renowned architect E.J. Lennox, known for his iconic designs in Toronto, was commissioned to create a structure that would harmonize with its natural surroundings while exuding a grandeur befitting its purpose.
Lennox’s design embraced the Beaux-Arts style, a blend of classical and Renaissance architectural elements. The symmetrical plan of the powerhouse featured a central block with a commanding Ionic portico flanked by two lengthy Ionic colonnades. The use of limestone for the exterior facade added to the station’s palatial appearance, seamlessly integrating it into the scenic landscape.
Engineering Marvels
Discovering the innovative engineering solutions employed in the construction of the Toronto Power Generation Station.
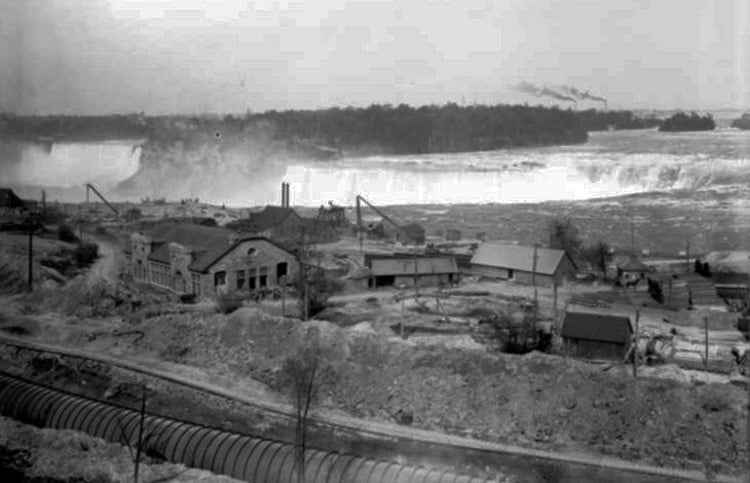
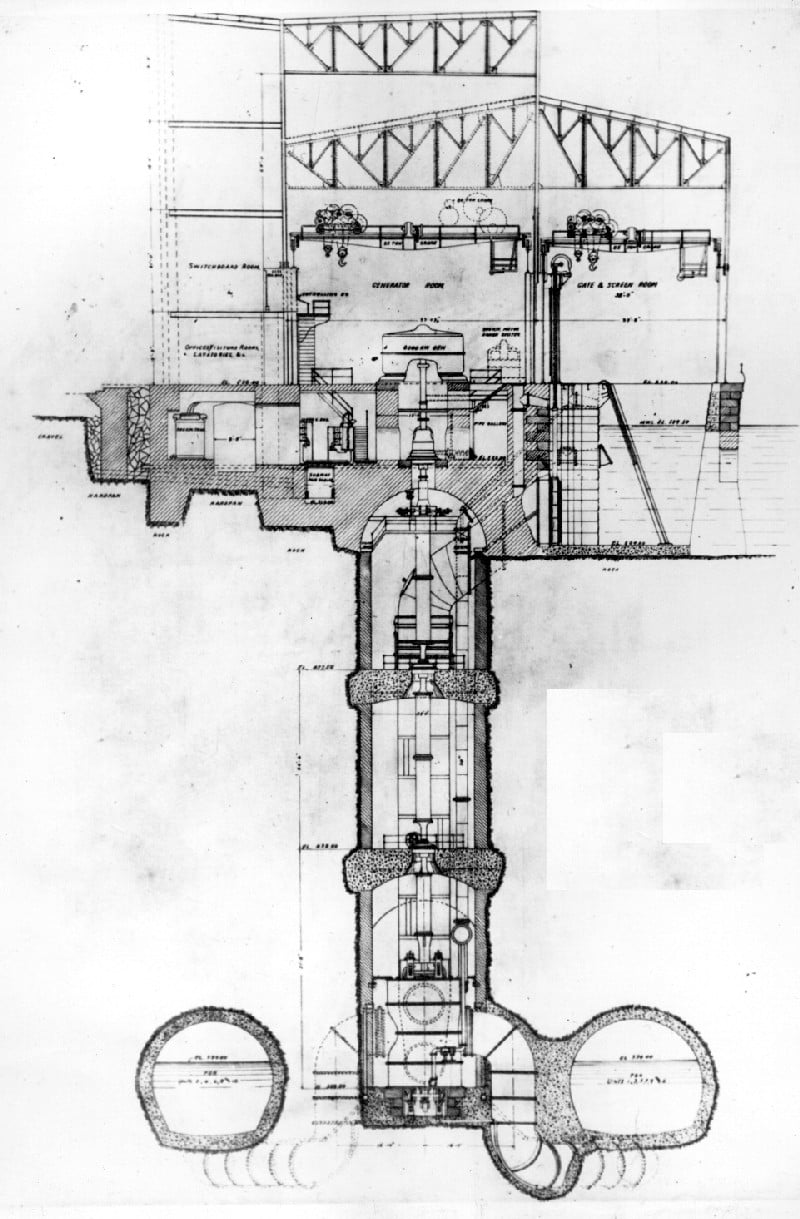
The Toronto Power Generation Station was not only a masterpiece of architecture but also a feat of engineering ingenuity. Engineers faced numerous challenges in adapting advanced technologies to the demanding site.
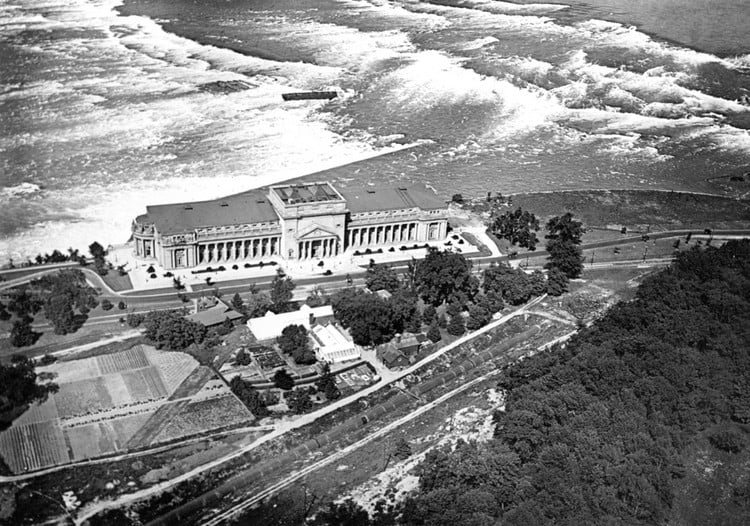
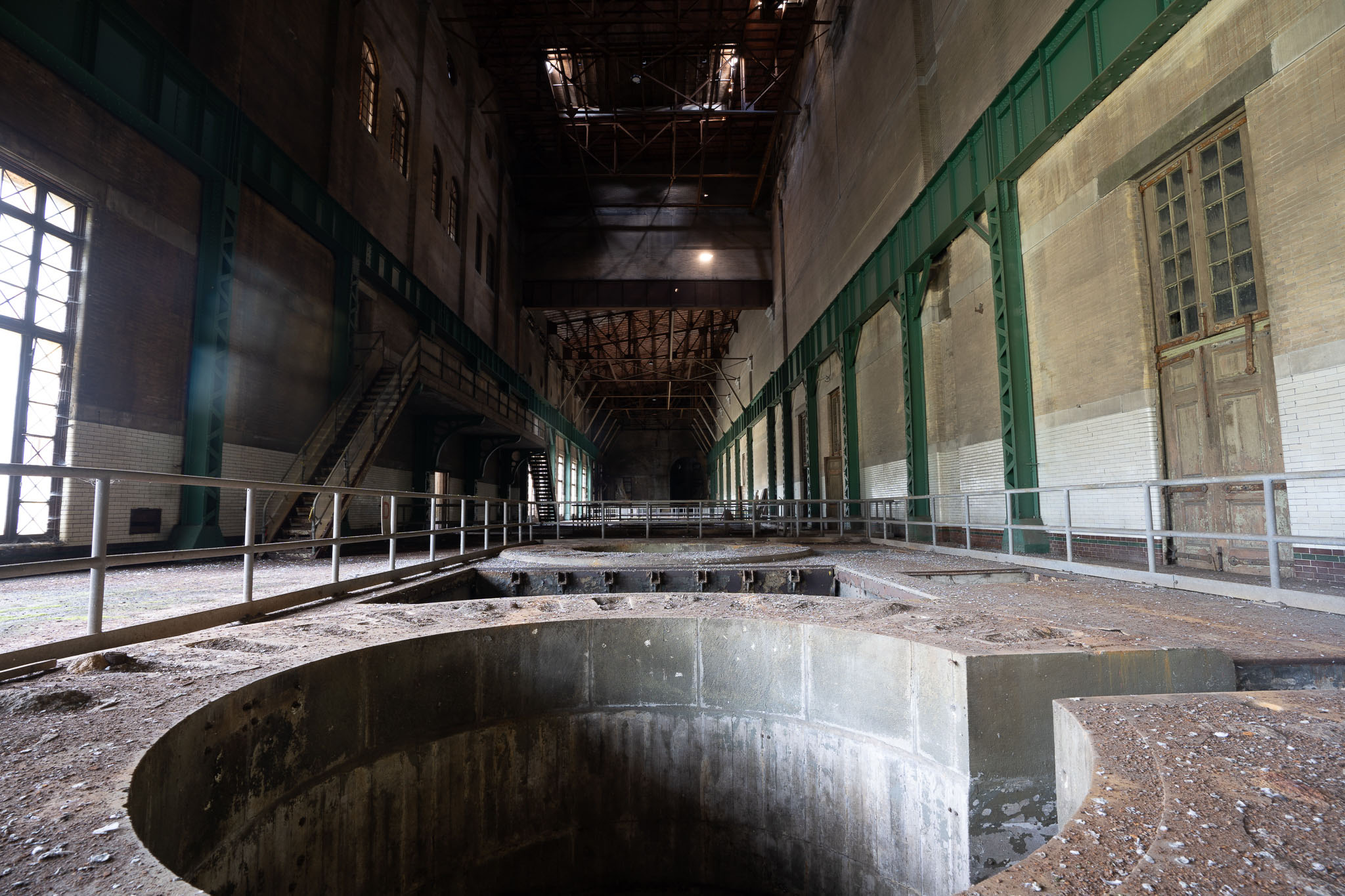
The heart of the station lay in the wheel pit, a deep chamber housing the turbines and generators. Vertical shafts connected the turbines at the bottom of the pit to the generators at the top. The water from the turbines flowed through a brick-lined tailrace, ultimately returning to the Niagara River.
The construction crews overcame obstacles with limited tools and resources, employing dynamite, pickaxes, shovels, and literal horsepower. The process involved excavating the wheel pit, constructing the tailrace tunnel, and creating a submerged dam and penstocks. These components had to be meticulously coordinated to ensure the seamless operation of the power station.
Hydroelectric Power Revolution
Unveiling the transformative impact of the Toronto Power Generation Station on the production and distribution of electricity.
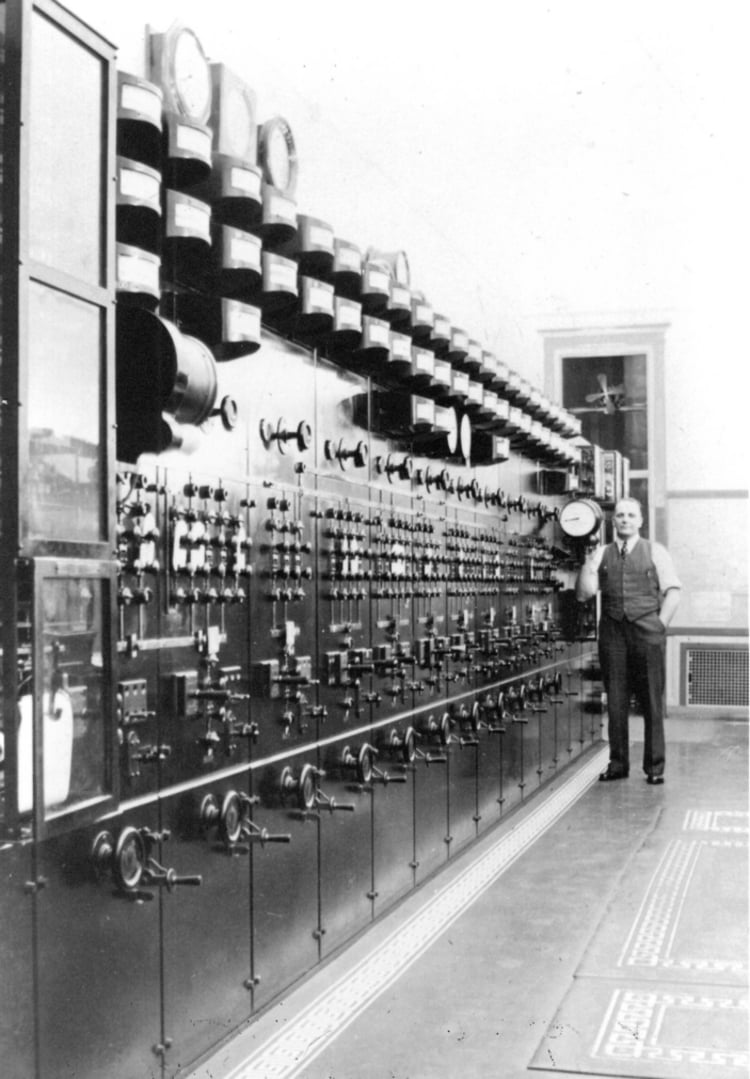
The completion of the Toronto Power Generation Station marked a turning point in the utilization of hydroelectric power in Canada. Its establishment allowed for the supply of hydroelectric power to the burgeoning city of Toronto, revolutionizing its industries and enhancing the quality of life for its residents.
With a generating capacity of 137,500 horsepower, the Toronto Power Generation Station became a vital source of electricity. It played a crucial role in powering factories, lighting streets, and fueling the growth of Toronto’s economy. The station’s operations contributed to the overall modernization and electrification of Ontario.
Ownership and Expansion
Tracing the ownership transitions and expansion of the Toronto Power Generation Station.
The Electrical Development Company of Ontario initially owned the Toronto Power Generation Station. However, in 1922, Ontario Hydro, the provincial power utility, acquired the station. Under Ontario Hydro’s stewardship, the station continued to provide electricity to Toronto and the surrounding areas.
Recognizing the growing demand for power, the station underwent expansions between 1913 and 1924. The initial 296-foot length was extended to 600 feet, accommodating additional generators. By 1924, eleven generators were in operation, reinforcing the station’s role as a major power producer.
End of an Era
Exploring the factors that led to the closure of the Toronto Power Generation Station.
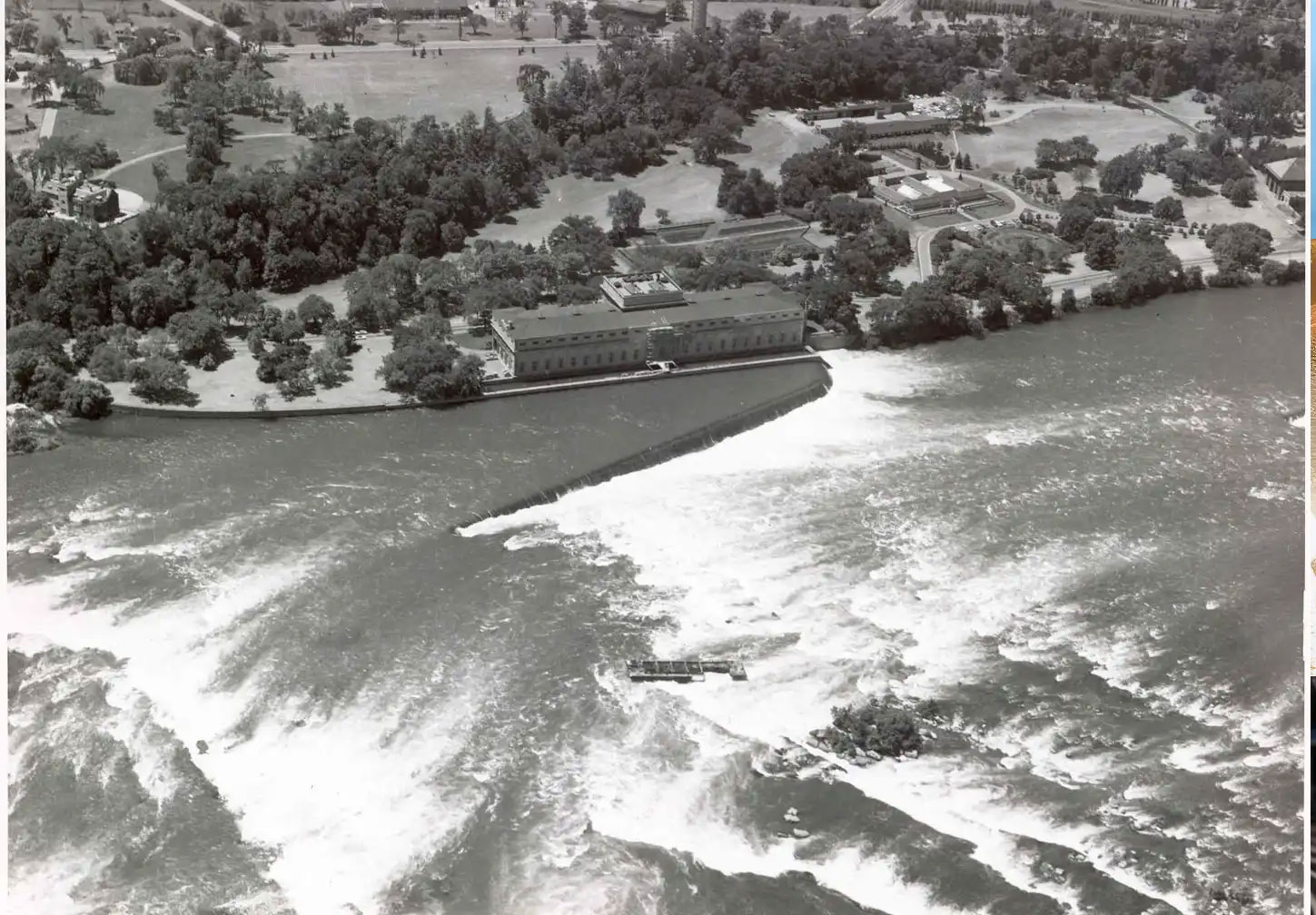
Despite its historical significance and remarkable achievements, the Toronto Power Generation Station ceased operations on February 15, 1974. Ontario Hydro made the decision to divert the available water resources downriver to the Sir Adam Beck Hydroelectric Power Stations in Queenston. Additionally, the plant produced electricity at a frequency of “25 Cycle,” which was no longer widely used.
The closure marked the end of an era for the Toronto Power Generation Station. After nearly seven decades of powering Toronto and contributing to the province’s industrial growth, the station fell silent.
National Historic Site Designation
Highlighting the recognition and preservation efforts for the Toronto Power Generation Station.
The Toronto Power Generation Station’s historical and architectural significance led to its designation as a National Historic Site of Canada in 1983. This recognition acknowledged its pivotal role in the development of hydroelectric power in Ontario and Canada, as well as the innovative application of Beaux-Arts design to an industrial setting.
In 2007, ownership of the Toronto Power Generation Station was transferred to the Niagara Parks Commission. Structural assessments were conducted to explore potential adaptive reuse options for the vacant facility.
Urban Exploration and Heritage Tourism
The allure of urban exploration and the future of the Toronto Power Generation Station.
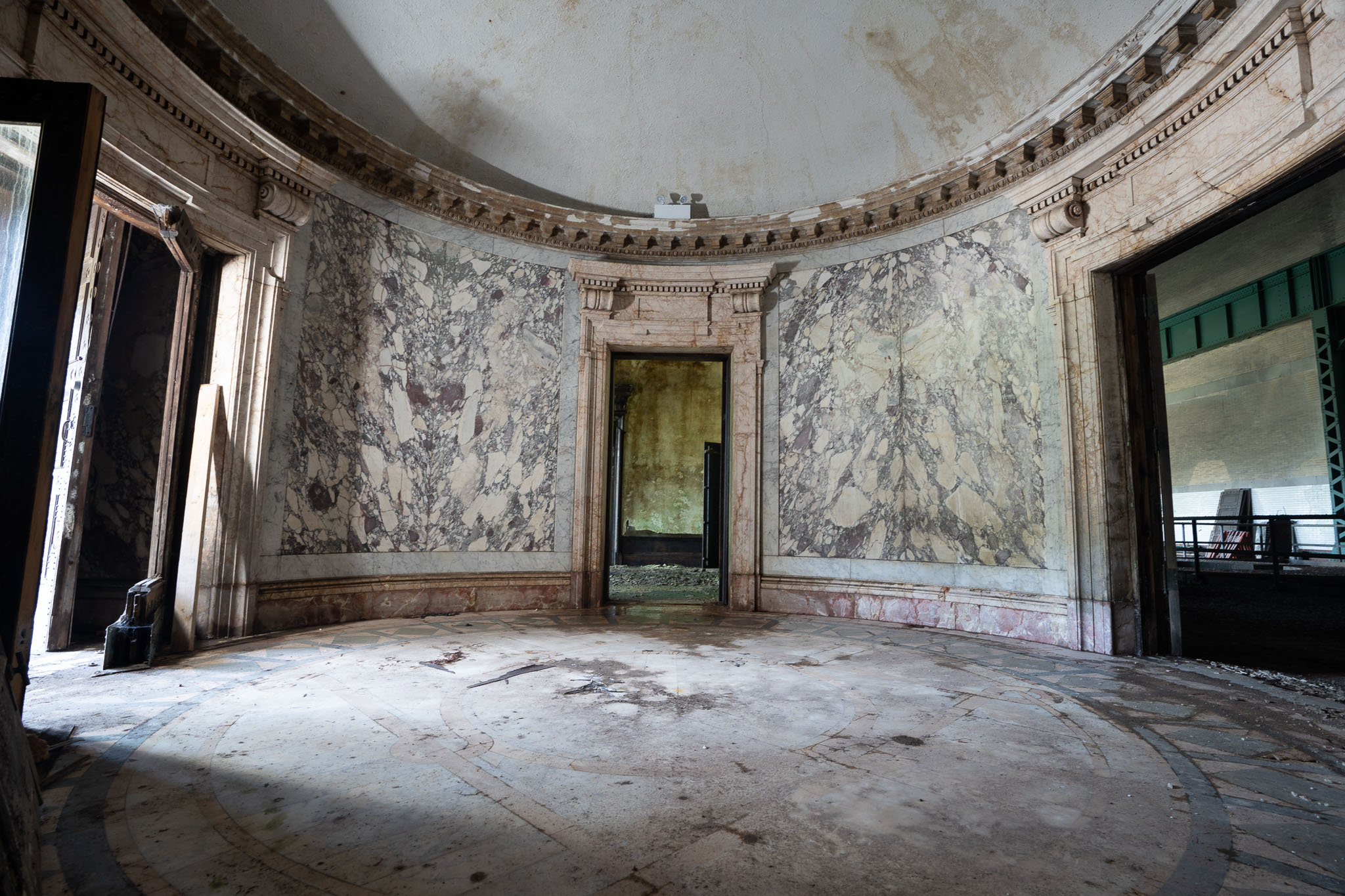
During its period of vacancy, the Toronto Power Generation Station emerged as a magnet for urban explorers. These daring individuals, deeply intrigued by this abandoned marvel, were willing to flout local laws, trespassing into the untouched structure to witness the remnants of its impressive machinery and immerse themselves in the atmosphere of a bygone era.
Recognizing the site’s potential, the Niagara Parks Commission thoroughly explored the prospects for heritage tourism at the Toronto Power Generation Station and recently completed a three-stage public procurement process. This process revealed Pearle Hospitality as the visionary proponent for the restoration and redevelopment of the historic station. The recent agreement with Pearle Hospitality underscores the commitment to restore and revitalize the property, ensuring that its heritage is not only celebrated but also preserved for future generations.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the enduring legacy of the Toronto Power Generation Station.
The Toronto Power Generation Station stands as a testament to Canada’s pioneering spirit and engineering prowess. From its bold architectural design to its innovative engineering solutions, the station embodies the remarkable achievements of early hydroelectric power generation.
While the Toronto Power Generation Station may no longer generate electricity, its historical significance and architectural splendor continues to captivate. As a National Historic Site, it serves as a reminder of the transformative power of electricity and the ingenuity of those who harnessed the might of Niagara Falls to illuminate and empower a growing nation.